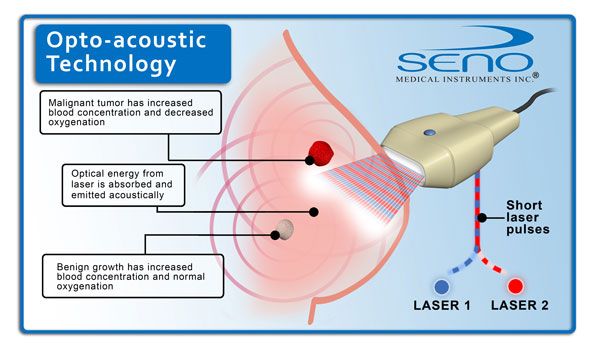
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING
Opto acoustic breast imaging is a new generation diagnostic tool currently in the clinical trial stage for diagnosis of malignant or benign breast lumps. According to a European journal of breast cancer around 4 million new cases of breast cancer are detected every year with almost 80 percent of them turning out to be benign on laboratory testing. It is difficult for radiologists to rule out malignancy at the imaging stage. The cost of conducting surgical or core needle biopsy for every suspicious lump outweighs the results especially in women coming from struggling economies. A low cost diagnostic tool such as opto acoustic imaging can help in the timely detection of breast cancer in the early stages and also help prevent and control the increasing mortality due to this disease in developing as well as developed countries.