Tips on Immobilization of Pediatric Patients for Radiography
Pediatric radiography presents unique challenges that require specialized techniques to ensure high-quality imaging and safety. The small and often uncooperative nature of pediatric patients makes it crucial to manage their movements carefully during procedures. Short exposure times are a standard practice in pediatric radiography to minimize motion blur, a common issue when imaging energetic children. However, even with reduced exposure times, the need for precise immobilization remains critical to obtaining clear and useful diagnostic images.
Effective immobilization techniques not only help in reducing the likelihood of motion blur but also play a significant role in enhancing the overall diagnostic accuracy of the images. By securing the patient in a safe and comfortable position, radiographers can reduce the necessity for retakes, thus shortening the duration of the procedure and minimizing the stress experienced by young patients. More importantly, proper immobilization helps in significantly lowering the radiation dose received by the patient, as it allows for more targeted and efficient use of radiography.
There are various immobilization devices and strategies tailored specifically for pediatric patients. These range from simple padded supports to more sophisticated systems designed to hold the patient gently yet securely. Training and experience in pediatric care are essential for radiographers to select and apply the most appropriate method for each individual case, ensuring the child’s comfort and safety while achieving optimal imaging results.
Ultimately, the goal of these immobilization strategies is to protect the well-being of young patients while enabling healthcare providers to perform high-quality diagnostic imaging. It’s a delicate balance that requires technical skills, patience, and a compassionate approach from the radiography team.
1. Calming Techniques for Children and Parents
For radiologic technologists, creating a welcoming and calm environment for young patients and their guardians is crucial. The experience of undergoing radiographic procedures like X-rays or MRIs can be intimidating for children, making it essential for medical professionals to actively foster a reassuring setting right from the reception area to the radiography room.
Effective Communication
Effective communication is the cornerstone of reducing pediatric patient anxiety. Technologists should aim to demystify the process by explaining what will happen in a way that is easy to understand. This involves:
- Gently introducing the equipment
- Walking through the procedure itself
- Clearly explaining the necessity of staying still, often achieved through immobilization
It’s important to clarify that immobilization helps in acquiring clear images swiftly, thereby reducing the duration of the procedure and minimizing any discomfort.
Parental Involvement
Parents’ involvement is integral to a child’s comfort. Whenever possible, parents should be allowed to accompany their child to the radiography room. Their presence offers immense emotional support and can be a key factor in reducing procedural anxiety. For cases where safety regulations prevent parents from being in the room during the procedure, alternative measures can be taken:
- Maintaining eye contact through a window
- Using intercom systems for verbal reassurance
Child-Friendly Environment
The physical environment should also cater to a child’s sense of well-being. This can be achieved by:
- Decorating the room with bright, cheerful colors and patterns
- Providing sensory toys or tactile mats for physical comfort or distraction
- Incorporating technology such as digital tablets with child-friendly apps and videos
These elements engage a child’s interest and curiosity, making them less aware of the procedure taking place.
Soothing Audiovisual Aids
Using soothing audiovisual aids can further enhance comfort:
- Playing soft, calming music
- Displaying slow-moving visual scenes
Research shows that such sensory distractions can significantly decrease anxiety and pain perception in pediatric patients.
“Clear communication and a comforting environment are key to managing pediatric patient anxiety during radiographic procedures.” – CE4RT
Staff Training
Training staff in pediatric care techniques that include empathy, patience, and effective distraction methods is vital. Radiologic technologists who are skilled in these areas are better equipped to manage young patients’ needs and ensure a positive, fear-free experience.
Conclusion
By integrating these thoughtful and compassionate strategies, radiologic technologists can significantly improve the procedural experience for children, thereby enhancing patient and parent satisfaction in radiographic services.
For more information on pediatric radiography, check out our Pediatric Radiography Guide.
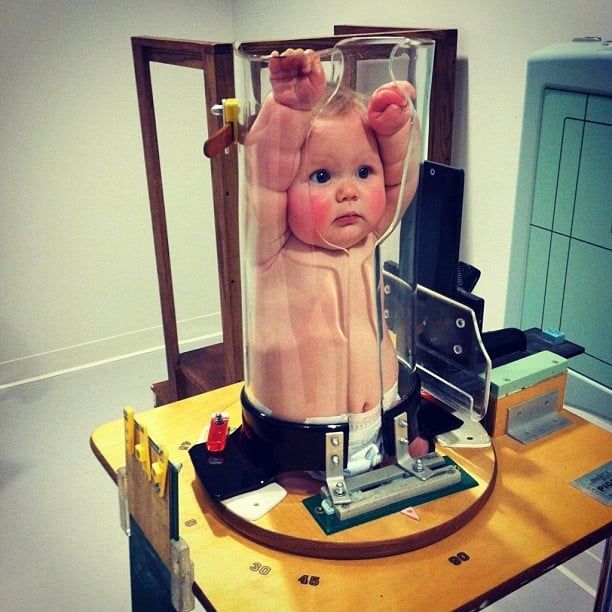
2. Transitioning Beyond the Pigg-O-Stat
The Pigg-O-Stat has long been a staple in pediatric radiography, providing an effective means of immobilizing young patients during X-ray procedures. Celebrated for its ability to quickly and securely position infants and young children, it has facilitated clearer imaging. However, as technology advances and patient comfort becomes a greater focus, the use of the Pigg-O-Stat is beginning to decline in favor of newer, more adaptable immobilization techniques.
Emerging Technologies
Newer immobilization technologies are gaining popularity in pediatric radiography. These innovations are specifically designed to meet the needs of more active and mobile infants, offering greater flexibility and comfort.
- Velcro Straps: These allow for adjustable tension, which can be finely tuned to accommodate the size and movement of the child, minimizing discomfort while ensuring safety.
- Radiolucent Foam Restraints: These restraints are transparent to X-rays, eliminating potential interference and improving the quality of diagnostic images.
Advantages of New Technologies
These newer immobilization methods offer several benefits over traditional devices like the Pigg-O-Stat:
- Enhanced comfort for young patients
- Greater flexibility in accommodating various sizes and movements
- Improved image quality due to the radiolucent properties of modern materials
- Alignment with modern healthcare practices that emphasize minimal restraint and maximal efficacy
“The shift towards newer immobilization technologies not only enhances patient comfort but also aligns with modern healthcare practices.” – CE4RT
Impact on Pediatric Radiography
As these technologies continue to evolve, they are set to redefine standards in pediatric radiography, making procedures quicker, safer, and less stressful for both patients and healthcare providers. The transition to these advanced techniques demonstrates a commitment to improving patient care and adapting to the needs of a younger, more active patient population.
Conclusion
The move away from traditional devices like the Pigg-O-Stat towards more innovative and patient-friendly immobilization methods marks a significant step forward in pediatric radiography. By embracing these new technologies, healthcare providers can ensure that their youngest patients receive the best possible care with minimal discomfort and maximal diagnostic accuracy.
For more insights on advancements in pediatric radiography, explore our article on Innovations in Pediatric Radiography.
3. Innovative DIY Immobilization Solutions
Resourcefulness in pediatric radiography often leads to effective and cost-efficient immobilization techniques using everyday materials. Creative solutions can be fashioned from items such as tape, towels, sandbags, and compression bands. When used properly, these materials can provide the necessary immobilization for precise imaging.
Materials for DIY Immobilization
Affordable and accessible materials can be utilized for effective immobilization:
- Tape: Useful for securing limbs but should be used with care to avoid skin irritation.
- Towels: Rolled and molded towels provide customized support and positioning.
- Sandbags: Weighty and malleable, they conform to the body’s contours for stable positioning.
- Compression Bands: Flexible and soft options ensure firm yet gentle restraint.
Protecting Delicate Skin
When employing DIY methods, it’s paramount to consider the delicate nature of an infant’s skin. To protect against potential irritation or damage:
- Soft Barriers: Place gauze under adhesive materials to cushion and reduce the risk of skin injury.
- Gentle Compression: Use flexible and soft compression bands to prevent movement without causing discomfort or harm.
“DIY immobilization solutions highlight the ingenuity of healthcare providers and ensure high-quality imaging, even in less-than-ideal circumstances.” – CE4RT
Custom Support with Towels and Sandbags
Towels and sandbags can be particularly useful for providing customized support and positioning:
- Towels: Rolled towels can be shaped to fit around the child’s body, offering stability without harsh pressure.
- Sandbags: Placed strategically, sandbags aid in immobilization by conforming to the patient’s body, avoiding direct contact that could lead to discomfort.
Conclusion
These innovative DIY solutions are a testament to the ingenuity of healthcare providers and the adaptability of pediatric radiographic practices. They ensure that high-quality imaging is achievable even in less-than-ideal circumstances, prioritizing patient safety and comfort throughout the process.
For more tips on pediatric radiography, visit our Tips for Pediatric Radiography page.
4. Advantages of Pedia-Poser
The Pedia-Poser, despite its robust and somewhat intimidating appearance, provides numerous advantages for immobilizing children from infancy through early childhood during various imaging procedures. Designed with precision and safety in mind, this device offers swift, adjustable immobilization that can adapt to the unique requirements of different diagnostic scenarios.
Swift and Adjustable Immobilization
Equipped with adjustable straps, the Pedia-Poser ensures that children of varying sizes are quickly and securely positioned. These straps can be easily tailored to fit snugly without being overly restrictive, minimizing discomfort and potential anxiety for the patient. The device’s ergonomic design helps maintain the child in the optimal position needed for clear imaging, thereby improving the quality of the results and reducing the likelihood of repeat scans.
Comfort and Safety Features
The materials used in the Pedia-Poser are specifically chosen to be gentle on delicate skin, ensuring that while the child is securely immobilized, there is no undue pressure or irritation. Key features include:
- Adjustable Straps: Tailored to fit snugly without restriction.
- Ergonomic Design: Maintains optimal positioning for clear imaging.
- Gentle Materials: Prevents pressure and irritation on delicate skin.
- Padded Elements: Enhances comfort and reduces distress.
“The Pedia-Poser’s thoughtful design integrates safety, comfort, and efficiency, making it an essential tool in pediatric radiography.” – CE4RT
Improved Imaging Quality
By ensuring the child is comfortably and securely positioned, the Pedia-Poser significantly enhances the quality of imaging. This reduces the need for repeat scans, thereby minimizing the child’s exposure to radiation and streamlining the diagnostic process.
Conclusion
In summary, the Pedia-Poser stands out as a leading choice in pediatric immobilization technology. Its thoughtful design integrates safety, comfort, and efficiency, making it an essential tool in pediatric radiography that ensures high-quality imaging with minimal distress for young patients.
For more information on pediatric radiography equipment, visit our Pediatric Radiography Equipment page.
5. Benefits of Swaddling Devices
Swaddling devices, such as Papooses and Infantainers, offer significant advantages in pediatric medical settings. Constructed from durable materials like Plexiglas or soft cushioning foam, these devices provide safe and effective immobilization for various procedures, including CT scans, radiographic exams, and minor surgeries. They ensure that young patients remain comfortable and secure, minimizing distress and movement.
Comfort and Security
Swaddling devices are designed to be both comfortable and secure, helping to minimize patient distress and movement during procedures. Key features include:
- Durable Materials: Constructed from Plexiglas or soft cushioning foam, ensuring longevity and patient comfort.
- Secure Fit: Keeps the child firmly in place, reducing anxiety and movement.
- Comfortable Design: Provides a snug fit without causing discomfort, aiding in patient relaxation.
Versatility in Positioning
The versatility of swaddling devices allows for various patient positioning, which is crucial for obtaining optimal imaging results or administering treatments precisely. This is especially important in pediatric care, where accommodating the small size and unique needs of infants and children is essential.
- Optimal Imaging: Ensures the patient remains still and properly aligned for clear imaging results.
- Precise Treatment: Facilitates accurate positioning for effective treatment administration.
Efficiency and Reduced Procedure Time
Using swaddling devices can significantly reduce the time needed for procedures by preventing movement and enabling more accurate initial positioning. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces the overall stress on the child and exposure to anesthesia or radiation, as applicable.
- Quick Setup: Easy to use and adjust, allowing for rapid patient preparation.
- Reduced Stress: Shorter procedure times decrease overall stress and exposure for young patients.
Ease of Use for Healthcare Providers
Swaddling devices are designed to be easy to use and adjust, assisting healthcare providers in quickly setting up and modifying the device to fit different patient sizes and needs. The materials used are chosen for their hypoallergenic properties and their ability to provide firm yet gentle restraint, ensuring the child’s comfort and safety throughout the procedure.
- Adjustable Straps: Easily modified to fit various patient sizes.
- Hypoallergenic Materials: Soft foam and other materials reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
- Firm Yet Gentle Restraint: Ensures safety without compromising comfort.
“Swaddling devices combine functionality with patient comfort, facilitating smoother, safer, and quicker medical processes.” – CE4RT
Conclusion
Overall, the benefits of swaddling devices in pediatric medical care are profound. They combine functionality with patient comfort, facilitating smoother, safer, and quicker medical processes. For more information on pediatric immobilization techniques, visit our Pediatric Immobilization Techniques page.
6. Parental Assistance in Pediatric Imaging
Incorporating parents in the imaging process as part of the immobilization strategy can be an effective approach, particularly for imaging extremities in children. This method leverages the comforting presence of parents to keep the child calm and still during the procedure. While simple and often effective, this technique requires careful consideration, especially for imaging the torso or head, where precision in positioning is critical and parent interaction needs to be managed carefully.
Safety Precautions
To ensure the safety of both parent and child, it is imperative that parents assisting in these procedures wear protective lead aprons and gloves. This protective gear is essential to shield them from radiation exposure during the imaging process. The safety and well-being of everyone involved are paramount, and such precautions help maintain these standards.
Factors Influencing Viability
The viability of parental assistance depends significantly on factors such as:
- Child’s Age: Younger children may benefit more from the presence of a parent.
- Child’s Cooperation: The ability of the child to stay calm and still.
- Imaging Procedure Demands: Specific requirements of the procedure being performed.
“Effective immobilization techniques are crucial for enhancing image clarity, reducing the need for retakes, and improving overall diagnostic accuracy.” – CE4RT
Choosing the Right Immobilization Devices
Radiologic technologists should choose immobilization devices and strategies that are:
- Simple to Implement: Easy and quick to assemble and disassemble.
- Non-impeding: Do not compromise the quality of imaging or safety.
Reducing Motion Blur
Pediatric radiography requires meticulous management to mitigate risks associated with patient movement during imaging. Using short exposure times is a common strategy to reduce motion blur. Despite these measures, achieving consistently clear images often demands additional strategies, such as:
- Effective Immobilization: Enhances image clarity and reduces retakes.
- Shorter Procedure Durations: Keeps young patients calm and cooperative.
- Minimized Radiation Exposure: Ensures safety for patients and staff, adhering to safety standards and reducing cumulative radiation dose.
Advanced and Child-Friendly Methods
By focusing on advanced and child-friendly immobilization methods, healthcare providers can secure the necessary imaging quality required for accurate diagnoses, while ensuring a safe and pleasant experience for their young patients. These strategies are indispensable in pediatric radiography where precision, patient comfort, and safety are paramount.
To learn more about optimizing pediatric radiography practices and minimizing radiation exposure, explore further details in our comprehensive guide at Reducing Radiation Exposure in Digital Imaging.
7. Advanced Positioning Techniques
Advanced positioning techniques in pediatric imaging represent a critical advancement in medical technology, aimed at reducing the reliance on sedation and improving the overall experience for young patients. These methods focus on enhancing both comfort and stability, which are essential for obtaining high-quality diagnostic images without the use of sedatives.
Elevated Platforms
One key component of these advanced techniques is the use of elevated platforms. These platforms are specifically designed to adjust to various heights and angles, accommodating patients of different sizes and the specific requirements of the imaging procedure.
- Adjustable Heights and Angles: Accommodate different patient sizes and imaging needs.
- Stable Base: Provides secure positioning to minimize movement and discomfort.
More about the benefits and designs of elevated platforms can be found at Elevated Platforms in Medical Imaging.
Customizable Positioning Aids
In addition to elevated platforms, customizable positioning aids play a vital role in pediatric imaging. These aids, including specially shaped cushions and adjustable supports, are tailored to fit the unique contours of young patients.
- Moldable Materials: Fit the body without causing pressure points.
- Enhanced Comfort: Ensures children remain still and comfortable, reducing the need for sedation.
Details on various customizable positioning aids and their applications can be explored at Customizable Positioning Aids for Pediatrics.
“Advanced positioning techniques not only enhance patient comfort but also reduce the need for sedation, making imaging procedures safer and quicker.” – CE4RT
Benefits of Advanced Techniques
The development and implementation of these advanced positioning techniques are driven by the goal of enhancing patient safety and comfort. By reducing the need for sedation, these techniques not only make the imaging process less invasive but also quicker and safer.
- Reduced Sedation: Minimizes invasiveness and associated risks.
- Improved Efficiency: Quicker procedures benefit both patients and healthcare providers.
Research on the impact of advanced positioning techniques on the need for pediatric sedation can be reviewed at Reducing Sedation in Pediatric Imaging.
Conclusion
Overall, the integration of advanced positioning techniques in pediatric imaging is transforming the way medical professionals approach diagnostics with young patients. These innovations provide the physical support needed during imaging procedures and reassure parents and guardians about the safety and efficacy of the medical care their children receive.
For more information on pediatric imaging practices, visit our Pediatric Imaging Practices page.
8. Engagement and Distraction Tools
In pediatric radiography, minimizing patient anxiety and movement is essential for capturing high-quality diagnostic images. One innovative approach to achieving this is through the use of engagement and distraction tools. These tools, including interactive games and virtual reality (VR) headsets, are designed to captivate young patients’ attention, thus significantly reducing their anxiety and involuntary movements during procedures.
Interactive Games
Interactive games are particularly effective as they not only entertain but also engage children in activities that require focus and calm. These games can be tailored to suit different age groups, ensuring that they are appropriate and captivating for toddlers through to older children.
- Engaging Activities: Games that require focus help keep children calm and still.
- Age-Appropriate Options: Tailored games ensure relevance and interest for all age groups.
- Integration: Touch screens and handheld controllers can be easily incorporated into the radiographic environment.
Further information on how interactive games can be used in medical settings can be found at Interactive Games in Medical Environments.
Virtual Reality (VR) Headsets
Virtual reality (VR) headsets offer a more immersive distraction by enveloping the child in a calm and engaging virtual world. Whether it’s a peaceful underwater scene or a gentle space adventure, VR can significantly divert the child’s focus from the clinical environment and the discomfort of the procedure.
- Immersive Experience: VR creates a captivating environment that distracts from the clinical setting.
- Focus Diversion: Reduces anxiety and movement during lengthy imaging sessions.
Research on the effectiveness of VR as a distraction tool in pediatric radiography can be explored at VR Health Applications.
“Distraction tools not only improve imaging quality by reducing movement but also enhance the overall patient experience.” – CE4RT
Improving Patient Experience
These distraction techniques not only improve the quality of the imaging by reducing movement but also enhance the overall patient experience. Less anxious children are more cooperative, leading to more efficient exams and reducing the likelihood of needing repeat scans due to poor initial outcomes.
- Efficient Exams: Reduced anxiety leads to more cooperative patients.
- Fewer Repeat Scans: High-quality initial images minimize the need for additional scans.
Insights into the impact of engagement and distraction tools on pediatric radiology efficiency can be found at Distraction Tools in Pediatric Radiology.
Conclusion
The deployment of these technologies in pediatric imaging centers is an example of how medical care is evolving to incorporate digital innovations that benefit patient care. By adopting these methods, healthcare providers can ensure a smoother procedure for young patients while achieving diagnostic accuracy necessary for effective treatment planning.
9. Training and Education for Technologists
For technologists specializing in pediatric radiography, ongoing training and education are not just beneficial—they are essential. Staying informed about the latest advancements in imaging technology, as well as deepening understanding of child psychology, equips technologists with the skills necessary to handle young patients with the utmost sensitivity and effectiveness.
Understanding Child Psychology
Understanding child psychology is particularly crucial in pediatric radiography. It enables technologists to anticipate the reactions of children to the imaging process and to adapt their approach accordingly. This knowledge helps in easing the fears and anxieties that children might experience in a clinical setting.
- Mitigating Fear: Techniques that reduce fear improve the child’s cooperation and the quality of imaging.
- Enhanced Experience: A better understanding of child psychology leads to a more positive experience for young patients.
Educational resources on child psychology in medical settings can be explored at Child Psychology in Healthcare.
Staying Updated on Immobilization Technologies
Continuous education on the latest immobilization technologies is vital. As new tools and techniques are developed, staying updated ensures that technologists can apply the most effective and least intrusive methods available.
- Enhanced Safety and Comfort: New technologies improve patient safety and comfort.
- Efficient Imaging Process: Using the latest methods enhances the efficiency of imaging procedures.
For the latest advancements in pediatric immobilization technology, visit Pediatric Immobilization Innovations.
Professional Training and Certifications
Many professional organizations offer specialized training programs and certifications for radiologic technologists working with children. These programs often include hands-on training in the latest pediatric imaging techniques, as well as seminars on patient interaction and safety protocols.
- Hands-On Training: Practical training in the latest pediatric imaging techniques.
- Safety Protocols: Seminars on patient interaction and safety.
Information on certification and training programs can be found at Radiology Certifications.
“Continuous professional development in pediatric radiography enhances the competencies of technologists and the quality of care provided to young patients.” – CE4RT
Conclusion
The commitment to continuous professional development in pediatric radiography not only enhances the competencies of technologists but also directly contributes to the quality of care provided to young patients. It ensures that medical imaging procedures are performed with precision, empathy, and respect for the unique needs of children.
10. Feedback Loop from Pediatric Patients
Implementing a comprehensive feedback system that gathers insights from young patients and their families about their imaging experiences is crucial for enhancing pediatric radiography practices. This feedback helps facilities identify what works well and what needs improvement, ensuring that the care provided is both effective and empathetic.
Establishing a Feedback Loop
To establish a robust feedback loop, medical facilities should deploy various tools tailored for easy engagement. Effective methods include:
- Digital Surveys: Sent via email to gather input post-visit.
- Tablet Surveys: User-friendly survey apps available at the clinic.
- Follow-Up Calls: Personal calls to discuss the experience.
These tools should be child-appropriate and parent-friendly, ensuring that even the youngest patients can express their perceptions. Comprehensive guidelines on designing and implementing these feedback systems can be found at Pediatric Feedback in Radiology.
Analyzing Feedback
Once collected, feedback should be meticulously analyzed to discern patterns and common issues. This analysis can lead to significant improvements in patient comfort, staff approachability, and the overall patient experience during radiographic exams.
- Identifying Patterns: Look for recurring themes in feedback.
- Implementing Improvements: Make necessary changes based on insights.
Techniques for effectively analyzing patient feedback can be explored further at Data Analysis in Healthcare.
“Regular feedback helps refine clinical practices and fosters a culture of continuous improvement and patient-centered care.” – CE4RT
Incorporating Feedback into Practice
Incorporating regular feedback into practice not only helps in refining clinical practices but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and patient-centered care. It encourages staff to be more responsive and adaptive to the needs of their patients, enhancing overall patient satisfaction and trust in healthcare services.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular updates and training based on feedback.
- Patient-Centered Care: Enhances satisfaction and trust in healthcare services.
Successful case studies on integrating feedback into healthcare practice can be reviewed at Healthcare Improvement Studies.
Engaging Parents
Maintaining an open line of communication through feedback allows parents to feel more involved in the healthcare processes affecting their children. This can be particularly comforting in the stressful environment of pediatric imaging.
- Parental Involvement: Involving parents in feedback loops enhances their comfort and trust.
- Effective Communication: Keeps parents informed and engaged in their child’s care.
Best practices for engaging parents in pediatric care feedback loops can be found at Parental Involvement in Healthcare.
Conclusion
Discover more about effective pediatric radiography practices at Reducing Radiation Exposure in Digital Imaging.
Pediatric radiography requires precise management to mitigate movement risks during imaging. Short exposure times are utilized to reduce blur caused by patient motion, yet challenges persist. Employing effective immobilization strategies is paramount to improve image clarity, reduce retakes, enhance diagnostic accuracy, and shorten procedure durations while also minimizing radiation exposure to everyone involved.
10. Feedback Loop from Pediatric Patients
Implementing a comprehensive feedback system that gathers insights from young patients and their families about their imaging experiences is crucial for enhancing pediatric radiography practices. This feedback helps facilities identify what works well and what needs improvement, ensuring that the care provided is both effective and empathetic.
Establishing a Feedback Loop
To establish a robust feedback loop, medical facilities should deploy various tools tailored for easy engagement. Effective methods include:
- Digital Surveys: Sent via email to gather input post-visit.
- Tablet Surveys: User-friendly survey apps available at the clinic.
- Follow-Up Calls: Personal calls to discuss the experience.
These tools should be child-appropriate and parent-friendly, ensuring that even the youngest patients can express their perceptions. Comprehensive guidelines on designing and implementing these feedback systems can be found at Pediatric Feedback in Radiology.
Analyzing Feedback
Once collected, feedback should be meticulously analyzed to discern patterns and common issues. This analysis can lead to significant improvements in patient comfort, staff approachability, and the overall patient experience during radiographic exams.
- Identifying Patterns: Look for recurring themes in feedback.
- Implementing Improvements: Make necessary changes based on insights.
Techniques for effectively analyzing patient feedback can be explored further at Data Analysis in Healthcare.
“Regular feedback helps refine clinical practices and fosters a culture of continuous improvement and patient-centered care.” – CE4RT
Incorporating Feedback into Practice
Incorporating regular feedback into practice not only helps in refining clinical practices but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and patient-centered care. It encourages staff to be more responsive and adaptive to the needs of their patients, enhancing overall patient satisfaction and trust in healthcare services.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular updates and training based on feedback.
- Patient-Centered Care: Enhances satisfaction and trust in healthcare services.
Successful case studies on integrating feedback into healthcare practice can be reviewed at Healthcare Improvement Studies.
Engaging Parents
Maintaining an open line of communication through feedback allows parents to feel more involved in the healthcare processes affecting their children. This can be particularly comforting in the stressful environment of pediatric imaging.
- Parental Involvement: Involving parents in feedback loops enhances their comfort and trust.
- Effective Communication: Keeps parents informed and engaged in their child’s care.
Best practices for engaging parents in pediatric care feedback loops can be found at Parental Involvement in Healthcare.
Conclusion
Discover more about effective pediatric radiography practices at Reducing Radiation Exposure in Digital Imaging.
11. Radiation Safety Measures
Radiation safety is paramount in pediatric radiography, where the vulnerability of young patients to ionizing radiation necessitates the most stringent protection protocols. Adopting rigorous safety measures and advanced techniques to minimize exposure is essential to safeguard health without compromising the quality of diagnostic imaging.
ALARA Principle
One fundamental practice is the use of the lowest effective radiation dose possible during imaging procedures. This approach, known as ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable), ensures that the radiation exposure is kept to the minimum necessary to obtain a clear diagnostic image.
- Careful Calibration: Regular calibration of imaging equipment to maintain optimal performance.
- Tailored Protocols: Selecting appropriate imaging protocols based on the patient’s size and diagnostic needs.
- Continuous Updates: Updating protocols based on the latest research.
For further information on implementing ALARA in pediatric radiography, visit ALARA Principles in Radiography.
Digital X-Ray Systems
Digital X-ray systems with dose reduction features represent another critical advancement in radiation safety. These systems optimize image quality while using significantly lower doses of radiation than traditional X-ray systems.
- Automatic Adjustments: Software that adjusts exposure settings based on the patient’s size and examination type.
- Minimized Exposure: Reduces unnecessary radiation exposure.
Details on the latest digital X-ray technologies can be found at Advancements in Digital Radiography.
Training for Radiologic Technologists
Rigorous training for radiologic technologists on dose management and safety practices is essential. This training ensures that all personnel involved in pediatric imaging are proficient in the latest safety standards and techniques.
- Professional Development: Continuous education on safety standards and dose management.
- Safety Techniques: Mastery of the latest methods to minimize radiation exposure.
Professional development resources for dose management training are available at Radiation Dose Management Training.
Educating Parents
Educating parents about the radiation safety measures being employed can significantly alleviate their concerns about the risks associated with radiographic procedures.
- Clear Communication: Explain how exposure is minimized and the steps taken to ensure safety.
- Building Trust: Helps foster understanding and confidence in the care provided.
Resources for educating parents on radiation safety can be accessed at Parental Radiation Safety Education.
“Adhering to rigorous radiation safety protocols ensures a high standard of care and safety for pediatric patients.” – CE4RT
Conclusion
By adhering to these rigorous radiation safety protocols and continuously educating both healthcare providers and parents, pediatric radiography facilities can ensure a high standard of care and safety for their youngest patients.
12. Customizable Immobilization Gear
The development and utilization of customizable immobilization gear are revolutionizing pediatric radiography. Tailored to fit different ages and sizes of pediatric patients, these innovative tools significantly enhance comfort and stability during imaging sessions. Such customization is vital in addressing the unique anatomical and psychological needs of children, ensuring better compliance and fewer movement artifacts during radiographic examinations.
Types of Customizable Immobilization Gear
Customizable immobilization gear includes a variety of devices, such as adjustable straps, contouring cushions, and modular support systems. These items are designed with flexible materials that can be easily adjusted to fit the precise shape and size of each child, providing a secure yet comfortable hold.
- Adjustable Straps: Easily modifiable to fit different sizes.
- Contouring Cushions: Mold to the child’s body for enhanced comfort.
- Modular Support Systems: Provide versatile and secure immobilization.
The ability to adjust and mold these tools on a per-patient basis reduces anxiety and discomfort, minimizing movement and the need for repeat scans. For an in-depth look at the types of customizable immobilization gear available, visit Pediatric Immobilization Options.
Advanced Materials
This gear often incorporates advanced materials that are both lightweight and radiolucent, ensuring they do not interfere with imaging results. The use of such materials also enhances overall safety and comfort for the patient, crucial factors in pediatric care.
- Lightweight: Easy to handle and adjust.
- Radiolucent: Does not affect the quality of the images.
Additional information on the materials used in customizable immobilization gear can be found at Advanced Medical Materials.
Training for Technologists
Training for radiologic technologists in the proper use of customizable immobilization gear is paramount. Effective training ensures that technologists are proficient in adjusting and applying these tools in a manner that maximizes patient comfort and imaging efficiency.
- Proficiency: Ensures optimal use of immobilization tools.
- Efficiency: Enhances imaging quality and reduces procedure time.
Resources for training programs focused on the latest in immobilization technology are available at Immobilization Technique Training.
Educating Parents
Educating parents about the benefits and safety features of this gear can further alleviate concerns and foster a cooperative environment during imaging sessions. Parental understanding is essential as it contributes to the child’s ease, reducing stress for both the child and the parents.
- Clear Communication: Helps parents understand the importance and safety of immobilization gear.
- Reduced Stress: Promotes a more relaxed atmosphere during procedures.
Tips for effectively communicating with parents about these tools are provided at Communicating Medical Gear Benefits to Parents.
“Customizable immobilization gear meets the varied needs of young patients while providing enhanced comfort, reduced anxiety, and superior imaging outcomes.” – CE4RT
Conclusion
Customizable immobilization gear is a critical component in modern pediatric radiography. By continually developing and implementing these specialized tools, medical facilities can significantly improve the quality of care and diagnostic accuracy in pediatric imaging.
13. Role of Child Life Specialists
Child life specialists are invaluable members of the pediatric radiography team, providing crucial emotional support and effective distraction techniques that ease the imaging process for young patients. With their specialized training in child development and psychology, these professionals play a pivotal role in ensuring that children and their families experience as little stress as possible during radiographic procedures.
Preparing Children for Procedures
The primary function of a child life specialist is to prepare children for medical procedures through education and play-based learning. They use age-appropriate explanations to help children understand what will happen during the imaging, why it’s necessary, and how it works, demystifying the process and reducing fear.
- Age-Appropriate Explanations: Help children understand the procedure.
- Therapeutic Play Techniques: Allow children to express fears and anxieties constructively.
For more detailed information on the strategies used by child life specialists, visit Child Life Services.
Distraction Techniques During Imaging
During imaging sessions, child life specialists provide distraction techniques such as storytelling, video games, or music to keep the child engaged and calm. These distractions not only help in reducing the child’s anxiety but also minimize movement, thus enhancing the quality of imaging.
- Storytelling: Engages the child’s imagination.
- Video Games: Keeps the child occupied and still.
- Music: Provides a soothing background.
The effectiveness of these distraction methods and their impact on pediatric radiography can be explored at Pediatric Distraction Methods.
“Child life specialists use distraction techniques to reduce anxiety and improve imaging quality.” – CE4RT
Supporting the Family
Child life specialists support the family as a whole, offering reassurance and guidance to parents and siblings. Educating the family about the process and what to expect significantly contributes to reducing overall stress levels within the family unit.
- Parental Reassurance: Helps parents stay calm and supportive.
- Sibling Support: Addresses the needs of the whole family.
Resources for families to understand the role and techniques of child life specialists can be found at Family Education in Radiology.
Training and Professional Development
Child life specialists’ training and ongoing education are key to their effectiveness. They must stay updated on the latest advancements in pediatric healthcare and child
14. Use of Sedation and Its Alternatives
In pediatric radiography, sedation is traditionally used to ensure that young patients remain still during lengthy or complex imaging procedures. However, the inherent risks associated with sedation, including potential side effects and the stress of recovery, have driven the exploration and adoption of alternative technologies that minimize or eliminate the need for sedation altogether.
Motion-Freezing Technology
One such alternative is motion-freezing technology, which has revolutionized pediatric imaging. This advanced technology allows radiographic equipment to capture clear, high-quality images at high speeds, effectively “freezing” any motion that occurs during the scan. This rapid capture reduces the window for movement, thus decreasing the likelihood of blurs or artifacts in the images and often eliminating the need for sedation.
- High-Speed Imaging: Captures clear images quickly to reduce motion artifacts.
- Reduced Sedation Need: Minimizes the necessity for sedation.
For more information on motion-freezing technology in pediatric radiography, visit Motion Freezing Technology in Radiography.
Engaging Distraction Techniques
Other non-sedative approaches include the use of engaging distraction techniques and child-friendly imaging environments. Distraction methods, such as VR headsets, interactive games, or even simple audiovisual aids, can keep children entertained and focused away from the procedure, thereby reducing movement.
- VR Headsets: Immersive experiences that captivate the child’s attention.
- Interactive Games: Engage children and keep them still.
- Audiovisual Aids: Simple tools like music or videos to distract and calm patients.
More details on effective distraction techniques in pediatric imaging can be found at Distraction Techniques in Pediatric Imaging.
Child-Friendly Imaging Environments
Creating a child-friendly imaging environment is also a vital alternative to sedation. This involves designing radiography rooms to be visually appealing and less intimidating to young patients. Elements such as colorful wall decals, themed rooms, and even the presence of toys or characters can make a significant difference in a child’s comfort and willingness to remain still during procedures.
- Colorful Wall Decals: Visually engaging elements to comfort children.
- Themed Rooms: Environments designed around popular themes or characters.
- Toys and Characters: Familiar items that help ease anxiety.
Insights into creating child-friendly imaging environments can be explored at Child-Friendly Imaging Environments.
“Engaging distraction techniques and child-friendly environments can reduce the need for sedation in pediatric imaging.” – CE4RT
Training for Radiologic Technologists
Continuous education for radiologic technologists on the latest non-sedative techniques and technologies is essential. Training helps ensure that all imaging staff are proficient in these alternatives, maximizing the safety and comfort of pediatric patients.
- Latest Techniques: Keeps technologists updated on new methods and technologies.
- Professional Development: Ensures the highest standards of patient care.
Resources for professional development in non-sedative pediatric imaging practices can be accessed at Non-Sedative Imaging Techniques.
Conclusion
The shift towards using these innovative and safer alternatives to sedation in pediatric radiography not only enhances patient safety but also improves the overall experience for young patients and their families. By reducing the reliance on sedation, healthcare providers can offer more child-friendly and less invasive imaging solutions.
15. Proactive Communication Channels
Establishing proactive communication channels between radiology departments and pediatricians is crucial for optimizing the pediatric imaging process. These channels enhance collaboration and coordination, which are vital for effective pre-procedure planning and valuable post-procedure feedback. By improving the flow of information, these communication strategies can significantly enhance the overall quality and efficiency of pediatric radiographic services.
Effective Pre-Procedure Planning
Effective pre-procedure planning involves detailed discussions about the specific needs and medical history of the patient. Radiologists and pediatricians can exchange critical information such as previous imaging results, potential allergies, and any specific concerns that may affect the imaging procedure.
- Previous Imaging Results: Review past images for a comprehensive understanding.
- Potential Allergies: Identify any allergies that may impact the procedure.
- Specific Concerns: Address any unique needs of the child.
This collaboration ensures that the imaging is tailored to the individual needs of the child, minimizing risks and improving diagnostic accuracy. A resource for best practices in medical communication can be found at Effective Healthcare Communication.
Post-Procedure Feedback
Post-procedure feedback is essential for assessing the outcomes of the imaging and determining the next steps in the patient’s care plan. Radiology departments can provide pediatricians with detailed reports and, if necessary, recommendations for further evaluations or treatments.
- Detailed Reports: Offer comprehensive analysis of imaging results.
- Recommendations: Suggest further evaluations or treatments as needed.
This ongoing exchange of information helps in refining treatment strategies and ensures continuous improvement in patient care. Insights into improving post-procedure communication in pediatric radiology can be explored at Post-Procedure Communication in Healthcare.
Modern Technology in Communication
Modern technology facilitates these communication channels through secure digital platforms that allow for the real-time exchange of patient data and imaging results. Systems such as electronic health records (EHRs) and picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) can be integrated to provide seamless access to patient information.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Provide comprehensive patient data access.
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): Facilitate image sharing and review.
More about integrating communication technologies in radiology can be found at Radiology Communication Technologies.
“Proactive communication channels enhance preparation for and follow-up after radiographic procedures, leading to improved patient outcomes.” – CE4RT
Training Programs
Training programs for radiologists and pediatricians on the use of these communication tools and strategies are also vital. They ensure that all healthcare providers involved are proficient in utilizing the systems effectively, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of patient information.
- Proficient Use: Ensure effective utilization of communication tools.
- Confidentiality: Maintain the integrity of patient information.
Training resources can be accessed at Medical Communication Training.
Conclusion
In summary, proactive communication channels between radiology departments and pediatricians are fundamental to a successful pediatric imaging process. They enhance the preparation for and follow-up after radiographic procedures, leading to improved patient outcomes and streamlined healthcare services.
16. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies into pediatric radiography represents a significant advancement in the field, offering unprecedented improvements in both efficiency and image quality. These technologies can automatically optimize imaging parameters for each patient, considering variables such as size, age, and specific diagnostic requirements, thus ensuring optimal results tailored to each clinical situation.
AI-Driven Optimization
AI algorithms are particularly adept at analyzing vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. In pediatric radiography, AI can automatically adjust exposure settings, focus, and other critical parameters in real-time.
- Optimized Exposure Settings: AI adjusts settings for clarity and detail.
- Reduced Radiation Dose: Ensures minimal exposure while maintaining image quality.
For more information on how AI is transforming pediatric imaging, visit AI-Powered Pediatric Imaging.
Machine Learning Enhancements
Machine learning models further enhance these capabilities by learning from each imaging session. Over time, these models can predict the best imaging settings based on previous successful outcomes, continuously improving the precision and efficiency of the imaging process.
- Learning from Data: ML models improve with each imaging session.
- Adaptive Imaging Settings: Continuously updated to reflect the latest techniques.
Detailed insights into the application of machine learning in radiology can be found at Machine Learning in Radiology.
Workflow Optimization
Beyond technical improvements, AI and ML also contribute to better patient management and workflow optimization. These technologies can automate parts of the diagnostic process, such as preliminary image analysis and identification of potential areas of concern.
- Automated Analysis: Reduces time per examination.
- Focus on Complex Cases: Allows radiologists to concentrate on more challenging diagnoses.
For a deeper understanding of workflow optimization through AI in radiology, visit AI in Radiology Workflow.
“AI and ML in pediatric radiography enhance image quality, reduce examination times, and improve patient care.” – CE4RT
Personalized Imaging Approaches
Integrating AI and ML into pediatric radiography can facilitate a more personalized approach to imaging. By analyzing data specific to pediatric patients, these technologies help develop protocols that minimize discomfort and stress during the imaging process.
- Personalized Protocols: Tailored to individual patient needs.
- Minimized Discomfort: Reduces stress for young patients.
Resources on personalized imaging strategies can be accessed at Personalized Imaging Strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of AI and machine learning into pediatric radiography is transforming the field by enhancing image quality, reducing examination times, and improving patient care through smarter, more efficient practices. This integration is pivotal in pushing the boundaries of what is possible in pediatric diagnostic imaging.
17. Continuous Quality Improvement Programs
Continuous quality improvement (CQI) programs are essential in pediatric radiography, ensuring that diagnostic practices evolve alongside the latest research and technological advancements. These programs involve systematic efforts to review, assess, and enhance radiographic procedures to uphold and enhance the standards of care and patient safety.
Iterative Improvement and Feedback
At the core of CQI programs is the principle of iterative improvement, where feedback from various stakeholders—including patients, families, radiologists, and technologists—is integrated into the radiographic process. This feedback loop is crucial for identifying areas where changes are necessary and for implementing solutions that address these needs effectively.
- Stakeholder Feedback: Gather input from all parties involved in the radiographic process.
- Effective Solutions: Implement changes based on feedback to improve practices.
For more information on establishing effective feedback systems in healthcare, visit Healthcare Feedback Systems.
Data Analytics for Improvement
CQI programs often utilize data analytics to monitor outcomes and identify trends that may indicate areas for improvement. By analyzing data related to procedure times, patient outcomes, and satisfaction levels, institutions can implement targeted interventions to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and improve patient experiences.
- Outcome Monitoring: Track and analyze data to identify improvement areas.
- Targeted Interventions: Use insights to enhance efficiency and patient care.
Resources on integrating data analytics into quality improvement can be found at Clinical Data Analytics.
Training and Development
Training and development are also integral components of CQI. Continuous education for radiology staff on the latest imaging techniques, safety protocols, and patient interaction strategies ensures that the quality of care keeps pace with advancements in the field. Moreover, training programs tailored to pediatric radiography focus on the unique challenges and requirements of imaging young patients.
- Continuous Education: Keep radiology staff updated on the latest techniques and protocols.
- Specialized Training: Focus on the unique needs of pediatric imaging.
For advanced training resources, check out Radiology Education Continuum.
Regular Protocol Reviews
Regularly scheduled reviews and updates to radiographic protocols based on the latest scientific research and technological innovations ensure that pediatric imaging practices remain current and optimal. This proactive approach not only enhances patient safety but also ensures high-quality imaging results.
- Protocol Updates: Regularly update protocols to reflect the latest research.
- Enhanced Safety: Maintain high standards for patient safety and imaging quality.
Information on the latest advancements in pediatric radiography can be accessed through Reducing Radiation Exposure in Digital Imaging.
“Continuous quality improvement programs ensure that diagnostic practices evolve with the latest advancements, enhancing standards of care and patient safety.” – CE4RT
Modern Technologies and Practices
Modern technologies such as 3D imaging and advanced MRI techniques have transformed pediatric radiography, offering detailed visuals without the need for invasive procedures or prolonged exposure to radiation. These technologies allow for quicker scans, which is especially beneficial for young patients who may find it difficult to remain still for long periods.
- 3D Imaging: Provides detailed visuals with minimal radiation exposure.
- Advanced MRI: Quick scans reduce the need for sedation.
For an overview of the latest advancements in imaging technology, visit Innovative Imaging Technology.
Artificial Intelligence in Radiography
The role of artificial intelligence (AI) in pediatric radiography cannot be understated. AI algorithms are increasingly used to optimize scan settings based on the patient’s age, size, and specific health concerns, ensuring high-quality images with minimal radiation exposure. AI also assists in faster image processing and interpretation, speeding up diagnosis and allowing for timely treatment decisions.
- Optimized Scan Settings: AI adjusts settings for each patient to ensure quality and safety.
- Faster Processing: AI speeds up image analysis and diagnosis.
Further information on AI applications in pediatric radiography can be found at AI in Pediatric Radiology.
Effective Communication
Effective communication remains a cornerstone of pediatric radiology, ensuring that both patients and their caregivers are adequately informed about the procedures. Clear explanations, visual aids, and child-friendly language help reduce anxiety and foster a cooperative atmosphere. Continuous education for radiologists and technologists on communication strategies is essential for maintaining empathy and professionalism in patient interactions.
- Clear Explanations: Help patients and caregivers understand procedures.
- Visual Aids: Use visuals to explain complex information.
- Child-Friendly Language: Communicate effectively with young patients.
Resources for enhancing communication skills in radiology can be accessed at Radiology Communication.
Ongoing Education and Training
To uphold high standards in pediatric radiological practices, ongoing education and training are imperative. This includes staying current with technological advancements, mastering new imaging techniques, and understanding the psychosocial aspects of dealing with pediatric patients. Comprehensive training programs and certification courses designed specifically for pediatric radiography professionals are available at Pediatric Radiography Education.
- Technological Advancements: Stay updated with the latest innovations.
- New Imaging Techniques: Master new methods and practices.
- Psychosocial Understanding: Address the unique needs of pediatric patients.
“Integrating innovative solutions and effective communication strategies enhances the quality of care and ensures a positive experience for young patients.” – CE4RT
Conclusion
The integration of innovative solutions and effective communication strategies in pediatric radiography not only enhances the quality of care provided but also ensures a more positive and less traumatic experience for young patients and their families.
Explore cutting-edge techniques and patient-centric strategies in pediatric radiography at Reducing Radiation Exposure in Digital Imaging.
This continuation delves deeper into the evolving field of pediatric radiography, focusing on the integration of modern technologies and practices that enhance the imaging experience for young patients. As medical imaging technology progresses, it’s crucial to adopt these innovations not only to improve diagnostic accuracy but also to ensure patient comfort and safety during procedures.
FAQs: Immobilization of Pediatric Patients for Radiography
- Q: Why is immobilization important for pediatric patients during radiography?
- A: Immobilization is crucial for pediatric patients during radiography to ensure high-quality images and accurate diagnoses. Children may find it difficult to stay still, and movement can lead to blurred images, necessitating repeat exposures and increasing radiation dose.
- Q: What are common techniques used for immobilizing pediatric patients?
- A: Common techniques include using physical restraints like swaddling, papoose boards, and Velcro straps, as well as distraction methods such as toys, videos, and talking to the child. In some cases, gentle holding by a parent or healthcare provider can also be effective.
- Q: How can radiographers ensure the comfort and safety of pediatric patients during immobilization?
- A: Radiographers can ensure comfort and safety by explaining the procedure to the child and parents, using the least restrictive immobilization method necessary, and constantly monitoring the patient for signs of distress. Comfort measures like padding and maintaining a warm environment can also help.
- Q: What role do parents or guardians play in the immobilization process?
- A: Parents or guardians can play a supportive role by helping to calm and reassure the child. They can also assist with immobilization if appropriate and allowed by the facility’s policies. Their presence can provide emotional comfort and reduce anxiety for the child.
- Q: Are there any risks associated with immobilization techniques in pediatric radiography?
- A: While immobilization techniques are generally safe, improper use can lead to discomfort, anxiety, or injury. It’s important to use these techniques judiciously and ensure they are not overly restrictive or applied for longer than necessary.
- Q: How do radiographers choose the appropriate immobilization method for a pediatric patient?
- A: Radiographers choose the appropriate method based on the child’s age, size, and level of cooperation, as well as the specific imaging procedure. The goal is to use the least restrictive and most comfortable method that effectively prevents movement.
