Radiographic Positioning of the Elbow


Forearm AP
Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the radius and ulna and soft tissue of the forearm.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part Supinated hand and extended elbow. Palm Up. Humeral epicondyles should be equal distances from the the image receptor.
Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the middle potion of the forearm.
Video Credit : Radpositioning49
Forearm Lateral Lateromedial


Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones and soft tissue of the entire forearm.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part Flex the elbow to a 90 degree angle. Position the hand and wrist in a true lateral position with thumb up.
Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the middle portion of the forearm.
Video Credit : Radpositioning49
Elbow AP


Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones of the elbow and proximal forearm, as well as the distal humerus and the elbow joint and soft tissue of the elbow.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part Place the arm on the table with the elbow straight and the palm of hand straight up. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table. Extend the elbow and keep the hand supinated, palm up.
Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the joint of the elbow.
Video Credit : Radpositioning49
Elbow Lateral Lateromedial



Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones of the elbow and proximal forearm, as well as the distal humerus and the elbow joint and soft tissue of the elbow. Soft tissue of the fat pads should be visible. On an elbow X-ray, a fat pad sign suggests an occult fracture. It is caused by displacement of the fat pad around the elbow joint. Both anterior and posterior fat pad signs exist, and both can be found on the same X-ray.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part The arm bent 90 degrees, thumb up, and the humeral epicondyles should be 90-degrees to the plane of the the image receptor.
Central ray to the image receptor at the joint of the elbow.
Video Credit : Radpositioning49
Elbow AP Oblique Medial (Internal) Rotation


Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones of the elbow and proximal forearm, as well as the distal humerus and the elbow joint and soft tissue of the elbow in an oblique position.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part Extend the upper limb and place elbow in the center of the image receptor, hand prone. Rotate the hand medially / internally until the anterior surface of the elbow is at a 45-degree angle.
Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the joint of the elbow.
Video Credit : Radpositioning49
Elbow AP Oblique Lateral (external) rotation


Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones of the elbow and proximal forearm, as well as the distal humerus and the elbow joint and soft tissue of the elbow in an oblique position.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part Extend the upper limb and place elbow in the center of the image receptor, hand prone. Rotate the hand laterally / externally until the anterior surface of the elbow is at a 45-degree angle.
Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the joint of the elbow.
Video Credit : Radpositioning49
Elbow Distal Humerus AP PARTIAL FLEXION
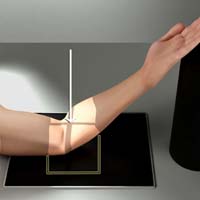
Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones and soft tissue of the elbow joint specifically the distal humerus.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part Elevate the forearm and put a support under it if needed. The long axis of the humerus should be resting on the horizontal plane of the image receptor on the table. Supinate the hand if the patient can do it.
Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the joint of the elbow.
Elbow Proximal Forearm AP Partial flexion

Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones and soft tissue of the proximal forearm and a partially opened elbow joint.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part Rest the forearm on the the table while keeping elbow slightly bent and the hand supinated.
Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the joint of the elbow.
Elbow Distal Humerus AP Acute flexion (JONES METHOD)



Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones and soft tissue of the elbow joint specifically the distal humerus, olecranon process free of superimposition, however the forearm and humerus are superimposed.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part Begin with anatomical AP with palm up, and have the patient fully flex the elbow if possible, or partially flexed as much as possible. Avoid rotation of the arm.
Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the joint of the elbow, or angled perpendicular to the forearm to better show the proximal forearm structures.
Elbow Radial Head Lateral Lateromedial




Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate the bones and soft tissue of the elbow joint specifically the radial head shown at different angle of rotations.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the arm on the table with elbow straight. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table.
Position of part The elbow joint should be flexed 90 degrees and positioned laterally.
First Exposure: Supinate hand as much as the patient can.
Second Exposure: Hand positioned laterally with the thumb on the upper surface.
Third exposure or Coyle Method: Hand is pronated.
Fourth exposure: Extreme internal rotation of the hand with the hand resting on the surface of the thumb.
Central ray The central ray should be perpendicular to the image receptor directed to the joint of the elbow. for a coyle method projection angle the tube 45 degrees.
Coyle Method

Video Credit : Radpositioning49
Video Credit : Radpositioning49
Elbow Distal Humerus or olecranon process PA Axial


Purpose and Structures Shown This view should demonstrate thebones and soft tissue of the elbow joint specifically the olecranon process and articular margin of the olecranon and humerus.
Position of patient The patient should be Seated sideways at the end of the the table. Place the elbow down on the image receptor. Ideally, the forearm should rest comfortably on the the image receptor.
Position of part Place the midway of the epicondyles at the the image receptor’s center. Flex the elbow and make the humerus at a 75 degree angle from the forearm. To avoid rotation of the humerus and ulna, supinate the hand and have the patient immobilize it using the other hand.
Central ray For the distal humerus, perpendicular to the image receptor directed to the ulnar sulcus, passing through the medial of the olecranon process. For the olecrenon process, perpendicular to the humerus at a 20 degree angle towards the wrist and directed at the olecranon process.
Visit here to know more about x-ray positioning and x ray of hand and finger.
