Radiographic Positioning Toes

This article discusses radiographic positioning to show the toes for the Radiologic Technologist (X-Ray Tech)
Toes AP
Purpose and Structures Shown Demonstrate distal phalanges. Does not show interphalangeal joint spaces as well as AP Axial. Phalanges of the toes not rotated. Toes separated. Distal ends of metatarsals. Soft tissues and bone detail.
Position of patient Seated or supine.
Position of part Dorsal surface of foot flat on IR.
Central ray Perpendicular to IR through the desired metatarsophalangeal joint.
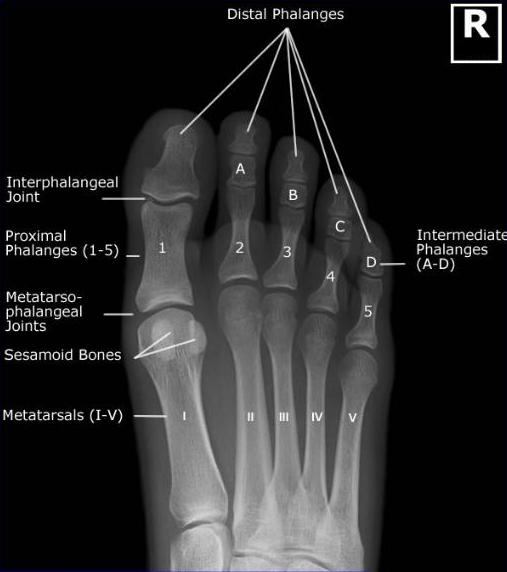
Toes AP Axial

Purpose and Structures Shown Demonstrate distal phalanges. Demonstrates interphalangeal joint spaces. Different from AP in that the CR is angled 15 degrees to show interphalangeal joints. Phalanges of the toes not rotated. Interphalangeal joint spaces. Distal ends of metatarsals.
Position of patient Seated or supine.
Position of part Dorsal surface of foot flat on IR. Toes separated.
Central ray 10 to 15 degrees posterior through the third metatarsophalangeal joint spaces. Tech can adjust beam angle based on body habitus and area of interest.
Toes AP Oblique

Purpose and Structures Shown Demonstrate distal phalanges Demonstrates interphalangeal joint spaces. Phalanges of the toes. Interphalangeal joints. Toes separated. Distal ends of metatarsals. Soft tissues and bone detail.
Position of patient Seated or Supine.
Position of part Center the toes on the IR. Medially rotate lower leg and foot. Tib-fib to form a 30- to 45-degree angle with the table. Central ray Perpendicular to IR at the metatarsophalangeal joints of interest. Toes PA Purpose and Structures Shown Demonstrate distal phalanges. Demonstrates interphalangeal joint spaces. Can be useful if patient must remain prone or for an alternative view. Phalanges of the toes. Interphalangeal joints. Phalanges not rotated. Toes separated. Distal ends of metatarsals. Soft tissues and bone detail. Position of patient Prone. Position of part Dorsal foot flat on table. Center toes on the IR
Central ray Perpendicular to IR at the third metatarsophalangeal joint.
Toes PA Oblique
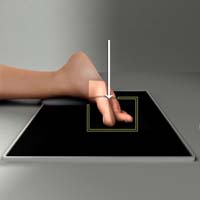
Purpose and Structures Shown Shows toes and distal portion of metatarsals rotated laterally. Toes and distal portion of the metatarsals rotated laterally. Phalanges of the toes. Interphalangeal joints. Toes separated. Distal ends of metatarsals. Soft tissues and bone detail.
Position of patient Lateral recumbent on affected side.
Position of part The affected limb should be adjusted in a partially extended position. Patient’s foot is turned from lateral, heel up toward the prone position until the ball of the foot to heel plane forms approximately a 30 to 45 degree angle with the IR plane. It may be useful to let the patient rest their foot on a sandbag or foam wedge.
Central ray Perpendicular to IR at third metatarsophalangeal joint.
Toes Lateral (Mediolateral or Lateromedial)

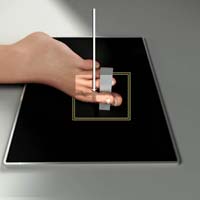
Purpose and Structures Shown Demonstrates lateral view of toes. Phalanges of the toes. Interphalangeal joints. Toes separated. Distal ends of metatarsals. Soft tissues and bone detail.
Position of patient Lateral recumbent on unaffected side. Support affected limb with sandbags and adjust in comfortable position.
Position of part Place toe in a true lateral position. Adjust long axis of IR, making parallel with long axis of toe. Adjust position of limb, placing toe of interest and IR or film in a parallel position, so that toe is as close to IR or film as possible. Support elevated heel on a sandbag or sponge to help keep still. Separate toes to avoid superimposition if needed. Consider using gauze pad, tongue depressor, or tape to separate toes.
Central ray Perpendicular to IR at metatarsophalangeal joint of great toe or proximal interphalangeal joint of lesser toes.
Toes Tangential Lewis Method (Sesamoids)

Purpose and Structures Shown To get tangential projection of metatarsal heads and sesamoid bones. Metatarsal head in profile. Sesamoid bones.
Position of patient Prone position. Raise ankle of affected side on sandbags for stability, if needed. For comfort, a folded towel may be placed under knee.
Position of part Dorsiflex great toe on table, adjust it to place ball of foot perpendicular to the horizontal plane. Center the IR to the second metatarsal.
Central ray Perpendicular to IR and tangential at the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
Toes Tangential Holly Method (Sesamoids)
Purpose and Structures Shown May be more comfortable for patient then Lewis method. Metatarsal head. Sesamoids.
Position of patient Seated on table.
Position of part Foot is adjusted so medial border is vertical. Plantar surface of toes at an angle of 75 degrees with plane of IR. Toes are held in a flexed position by patient (using a strip of bandage if needed).
Central ray Perpendicular to IR at head of first metatarsal bone.
Toes Tangential Causton Method (Sesamoids)
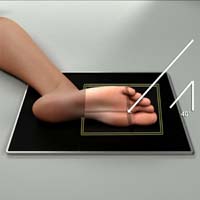
Purpose and Structures Shown To get tangential image that shows sesamoid bones projected axiolaterally with a slight overlap. Sesamoid bones.
Position of patient Lateral recumbent on unaffected side with knees flexed.
Position of part Limb being examined should be partially extended, with sandbags under knee and foot. Foot is placed in lateral position by adjusting sandbag’s height, with first metatarsophalangeal joint perpendicular to horizontal plane of IR. IR should be under distal metatarsal region and adjusted so that mid-point coincides with Central ray.
Central ray CR at prominence of first metatarsophalangeal joint at an angle of 40 degrees toward heel.
More Resources.
Video Credit : RadPositioning