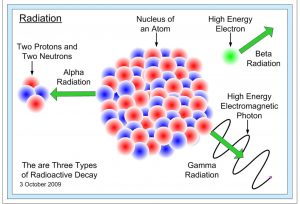
Techniques to Reduce Bone Densitometry Radiation Dose

In this article we talk about bone densitometry radiation dose and the techniques that radiologic technologists can apply to reduce it. The two key principles in patient radiation protection are justification and optimization. Justification implies that any X-ray exposure is justified clinically. It means the examinations that will not affect the patient’s care are avoided. Once an examination is justified, optimization consists of activities that reduce bone densitometry radiation dose. This means delivery of the smallest possible dose to the patient.